| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
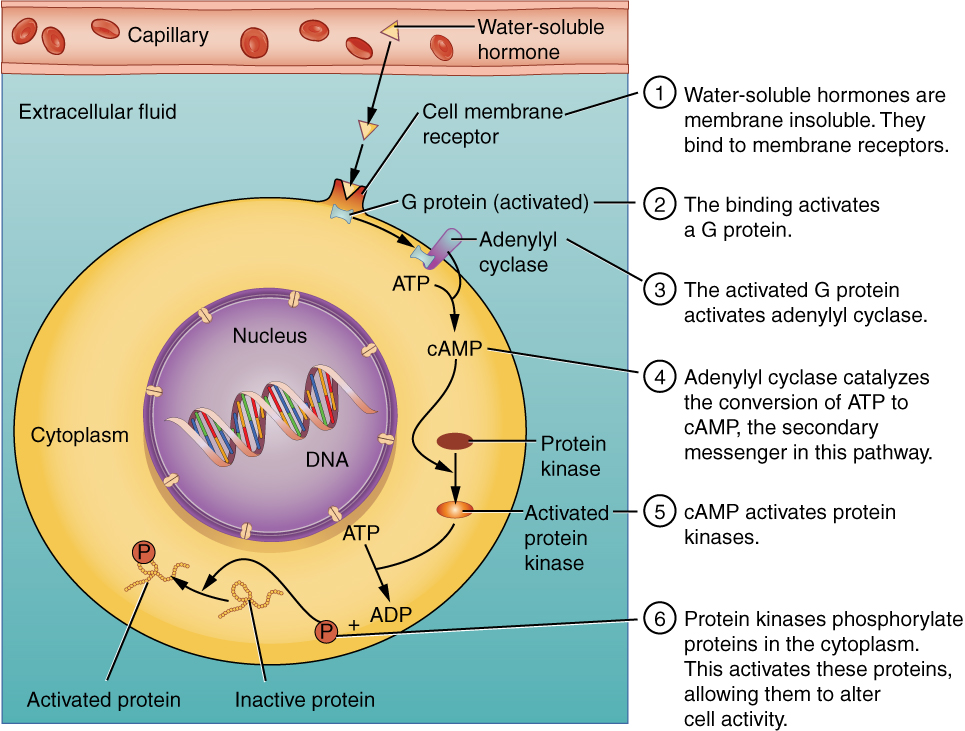
The phosphorylation of cellular proteins can trigger a wide variety of effects, from nutrient metabolism to the synthesis of different hormones and other products. The effects vary according to the type of target cell, the G proteins and kinases involved, and the phosphorylation of proteins. Examples of hormones that use cAMP as a second messenger include calcitonin, which is important for bone construction and regulating blood calcium levels; glucagon, which plays a role in blood glucose levels; and thyroid-stimulating hormone, which causes the release of T 3 and T 4 from the thyroid gland.
Overall, the phosphorylation cascade significantly increases the efficiency, speed, and specificity of the hormonal response, as thousands of signaling events can be initiated simultaneously in response to a very low concentration of hormone in the bloodstream. However, the duration of the hormone signal is short, as cAMP is quickly deactivated by the enzyme phosphodiesterase (PDE) , which is located in the cytosol. The action of PDE helps to ensure that a target cell’s response ceases quickly unless new hormones arrive at the cell membrane.
Importantly, there are also G proteins that decrease the levels of cAMP in the cell in response to hormone binding. For example, when growth hormone–inhibiting hormone (GHIH), also known as somatostatin, binds to its receptors in the pituitary gland, the level of cAMP decreases, thereby inhibiting the secretion of human growth hormone.
Not all water-soluble hormones initiate the cAMP second messenger system. One common alternative system uses calcium ions as a second messenger. In this system, G proteins activate the enzyme phospholipase C (PLC), which functions similarly to adenylyl cyclase. Once activated, PLC cleaves a membrane-bound phospholipid into two molecules: diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol triphosphate (IP 3 ) . Like cAMP, DAG activates protein kinases that initiate a phosphorylation cascade. At the same time, IP 3 causes calcium ions to be released from storage sites within the cytosol, such as from within the smooth endoplasmic reticulum. The calcium ions then act as second messengers in two ways: they can influence enzymatic and other cellular activities directly, or they can bind to calcium-binding proteins, the most common of which is calmodulin. Upon binding calcium, calmodulin is able to modulate protein kinase within the cell. Examples of hormones that use calcium ions as a second messenger system include angiotensin II, which helps regulate blood pressure through vasoconstriction, and growth hormone–releasing hormone (GHRH), which causes the pituitary gland to release growth hormones.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?