| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
There are compounds with nitrogen in all of its oxidation states from 3− to 5+. Much of the chemistry of nitrogen involves oxidation-reduction reactions. Some active metals (such as alkali metals and alkaline earth metals) can reduce nitrogen to form metal nitrides. In the remainder of this section, we will examine nitrogen-oxygen chemistry.
There are well-characterized nitrogen oxides in which nitrogen exhibits each of its positive oxidation numbers from 1+ to 5+. When ammonium nitrate is carefully heated, nitrous oxide (dinitrogen oxide) and water vapor form. Stronger heating generates nitrogen gas, oxygen gas, and water vapor. No one should ever attempt this reaction—it can be very explosive. In 1947, there was a major ammonium nitrate explosion in Texas City, Texas, and, in 2013, there was another major explosion in West, Texas. In the last 100 years, there were nearly 30 similar disasters worldwide, resulting in the loss of numerous lives. In this oxidation-reduction reaction, the nitrogen in the nitrate ion oxidizes the nitrogen in the ammonium ion. Nitrous oxide, shown in [link] , is a colorless gas possessing a mild, pleasing odor and a sweet taste. It finds application as an anesthetic for minor operations, especially in dentistry, under the name “laughing gas.”
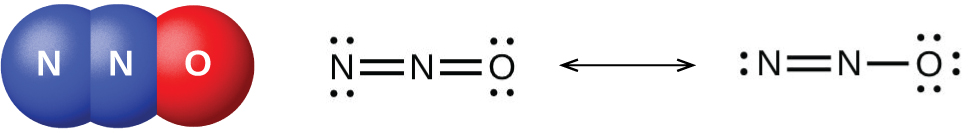
Low yields of nitric oxide, NO, form when heating nitrogen and oxygen together. NO also forms when lightning passes through air during thunderstorms. Burning ammonia is the commercial method of preparing nitric oxide. In the laboratory, the reduction of nitric acid is the best method for preparing nitric oxide. When copper reacts with dilute nitric acid, nitric oxide is the principal reduction product:
Gaseous nitric oxide is the most thermally stable of the nitrogen oxides and is the simplest known thermally stable molecule with an unpaired electron. It is one of the air pollutants generated by internal combustion engines, resulting from the reaction of atmospheric nitrogen and oxygen during the combustion process.
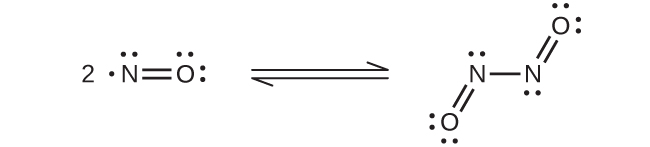
At room temperature, nitric oxide is a colorless gas consisting of diatomic molecules. As is often the case with molecules that contain an unpaired electron, two molecules combine to form a dimer by pairing their unpaired electrons to form a bond. Liquid and solid NO both contain N 2 O 2 dimers, like that shown in [link] . Most substances with unpaired electrons exhibit color by absorbing visible light; however, NO is colorless because the absorption of light is not in the visible region of the spectrum.
Cooling a mixture of equal parts nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide to −21 °C produces dinitrogen trioxide, a blue liquid consisting of N 2 O 3 molecules (shown in [link] ). Dinitrogen trioxide exists only in the liquid and solid states. When heated, it reverts to a mixture of NO and NO 2 .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?