| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The pentahalides of phosphorus are Lewis acids because of the empty valence d orbitals of phosphorus. These compounds readily react with halide ions (Lewis bases) to give the anion Whereas phosphorus pentafluoride is a molecular compound in all states, X-ray studies show that solid phosphorus pentachloride is an ionic compound, as are phosphorus pentabromide, [Br − ], and phosphorus pentaiodide, [I − ].
Phosphorus (group 15) commonly exhibits oxidation states of 3− with active metals and of 3+ and 5+ with more electronegative nonmetals. The halogens and oxygen will oxidize phosphorus. The oxides are phosphorus(V) oxide, P 4 O 10 , and phosphorus(III) oxide, P 4 O 6 . The two common methods for preparing orthophosphoric acid, H 3 PO 4 , are either the reaction of a phosphate with sulfuric acid or the reaction of water with phosphorus(V) oxide. Orthophosphoric acid is a triprotic acid that forms three types of salts.
Write the Lewis structure for each of the following. You may wish to review the chapter on chemical bonding and molecular geometry.
(a) PH 3
(b)
(c) P 2 H 4
(d)
(e) PF 5
(a)
 ;
;
(b)
 ;
;
(c)
 ;
;
(d)
 ;
;
(e)

Describe the molecular structure of each of the following molecules or ions listed. You may wish to review the chapter on chemical bonding and molecular geometry.
(a) PH 3
(b)
(c) P 2 H 4
(d)
Complete and balance each of the following chemical equations. (In some cases, there may be more than one correct answer.)
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
(f)
(a) (b) (c) (d) or (e) or (f)
Describe the hybridization of phosphorus in each of the following compounds: P 4 O 10 , P 4 O 6 , PH 4 I (an ionic compound), PBr 3 , H 3 PO 4 , H 3 PO 3 , PH 3 , and P 2 H 4 . You may wish to review the chapter on advanced theories of covalent bonding.
What volume of 0.200 M NaOH is necessary to neutralize the solution produced by dissolving 2.00 g of PCl 3 is an excess of water? Note that when H 3 PO 3 is titrated under these conditions, only one proton of the acid molecule reacts.
291 mL
How much POCl 3 can form from 25.0 g of PCl 5 and the appropriate amount of H 2 O?
How many tons of Ca 3 (PO 4 ) 2 are necessary to prepare 5.0 tons of phosphorus if the yield is 90%?
28 tons
Write equations showing the stepwise ionization of phosphorous acid.
Draw the Lewis structures and describe the geometry for the following:
(a)
(b) PF 5
(c)
(d) POF 3
(a)
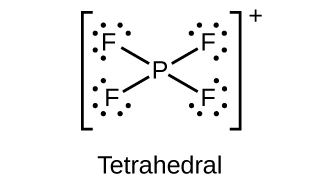 ;
;
(b)
 ;
;
(c)
 ;
;
(d)

Why does phosphorous acid form only two series of salts, even though the molecule contains three hydrogen atoms?
Assign an oxidation state to phosphorus in each of the following:
(a) NaH 2 PO 3
(b) PF 5
(c) P 4 O 6
(d) K 3 PO 4
(e) Na 3 P
(f) Na 4 P 2 O 7
(a) P = 3+; (b) P = 5+; (c) P = 3+; (d) P = 5+; (e) P = 3−; (f) P = 5+
Phosphoric acid, one of the acids used in some cola drinks, is produced by the reaction of phosphorus(V) oxide, an acidic oxide, with water. Phosphorus(V) oxide is prepared by the combustion of phosphorus.
(a) Write the empirical formula of phosphorus(V) oxide.
(b) What is the molecular formula of phosphorus(V) oxide if the molar mass is about 280.
(c) Write balanced equations for the production of phosphorus(V) oxide and phosphoric acid.
(d) Determine the mass of phosphorus required to make 1.00 10 4 kg of phosphoric acid, assuming a yield of 98.85%.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?