| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
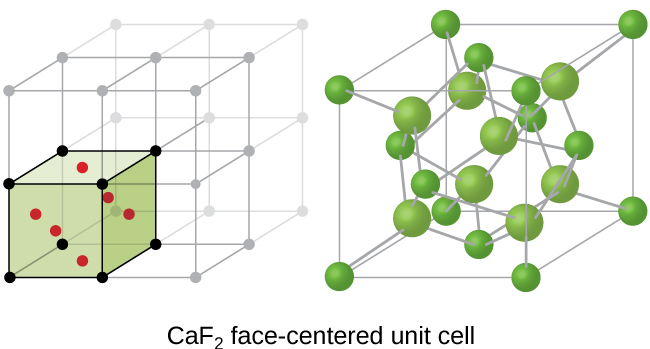
If we know the edge length of a unit cell of an ionic compound and the position of the ions in the cell, we can calculate ionic radii for the ions in the compound if we make assumptions about individual ionic shapes and contacts.
Note: The length unit angstrom, Å, is often used to represent atomic-scale dimensions and is equivalent to 10 −10 m.
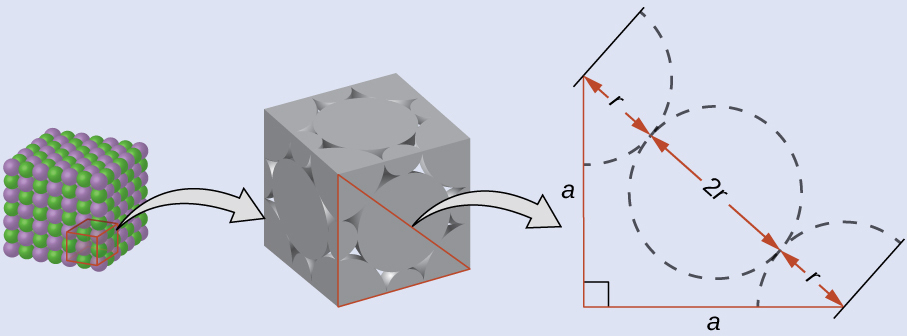
Drawing a right triangle on the face of the unit cell, we see that the length of the diagonal is equal to four chloride radii (one radius from each corner chloride and one diameter—which equals two radii—from the chloride ion in the center of the face), so d = 4 r . From the Pythagorean theorem, we have:
which yields:
Solving this gives:
The radius of the potassium ion is 1.33 Å.
It is important to realize that values for ionic radii calculated from the edge lengths of unit cells depend on numerous assumptions, such as a perfect spherical shape for ions, which are approximations at best. Hence, such calculated values are themselves approximate and comparisons cannot be pushed too far. Nevertheless, this method has proved useful for calculating ionic radii from experimental measurements such as X-ray crystallographic determinations.
The size of the unit cell and the arrangement of atoms in a crystal may be determined from measurements of the diffraction of X-rays by the crystal, termed X-ray crystallography . Diffraction is the change in the direction of travel experienced by an electromagnetic wave when it encounters a physical barrier whose dimensions are comparable to those of the wavelength of the light. X-rays are electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths about as long as the distance between neighboring atoms in crystals (on the order of a few Å).
When a beam of monochromatic X-rays strikes a crystal, its rays are scattered in all directions by the atoms within the crystal. When scattered waves traveling in the same direction encounter one another, they undergo interference , a process by which the waves combine to yield either an increase or a decrease in amplitude (intensity) depending upon the extent to which the combining waves’ maxima are separated (see [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?