| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
What is the mechanism by which one magnet exerts a force on another? The answer is related to the fact that all magnetism is caused by current, the flow of charge. Magnetic fields exert forces on moving charges , and so they exert forces on other magnets, all of which have moving charges.
The magnetic force on a moving charge is one of the most fundamental known. Magnetic force is as important as the electrostatic or Coulomb force. Yet the magnetic force is more complex, in both the number of factors that affects it and in its direction, than the relatively simple Coulomb force. The magnitude of the magnetic force on a charge moving at a speed in a magnetic field of strength is given by
where is the angle between the directions of and This force is often called the Lorentz force . In fact, this is how we define the magnetic field strength —in terms of the force on a charged particle moving in a magnetic field. The SI unit for magnetic field strength is called the tesla (T) after the eccentric but brilliant inventor Nikola Tesla (1856–1943). To determine how the tesla relates to other SI units, we solve for .
Because is unitless, the tesla is
(note that C/s = A).
Another smaller unit, called the gauss (G), where , is sometimes used. The strongest permanent magnets have fields near 2 T; superconducting electromagnets may attain 10 T or more. The Earth’s magnetic field on its surface is only about , or 0.5 G.
The direction of the magnetic force is perpendicular to the plane formed by and , as determined by the right hand rule 1 (or RHR-1), which is illustrated in [link] . RHR-1 states that, to determine the direction of the magnetic force on a positive moving charge, you point the thumb of the right hand in the direction of , the fingers in the direction of , and a perpendicular to the palm points in the direction of . One way to remember this is that there is one velocity, and so the thumb represents it. There are many field lines, and so the fingers represent them. The force is in the direction you would push with your palm. The force on a negative charge is in exactly the opposite direction to that on a positive charge.
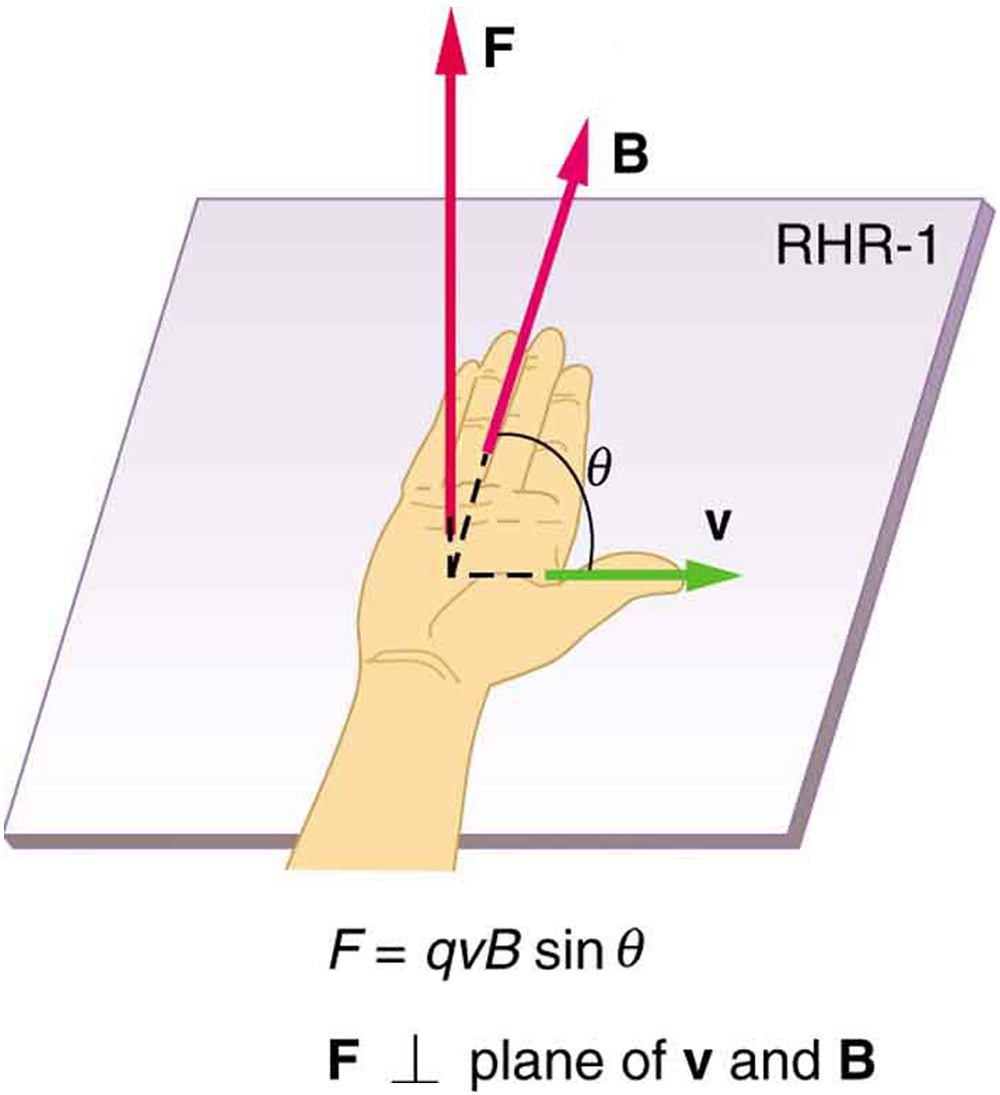
There is no magnetic force on static charges. However, there is a magnetic force on moving charges. When charges are stationary, their electric fields do not affect magnets. But, when charges move, they produce magnetic fields that exert forces on other magnets. When there is relative motion, a connection between electric and magnetic fields emerges—each affects the other.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?