| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
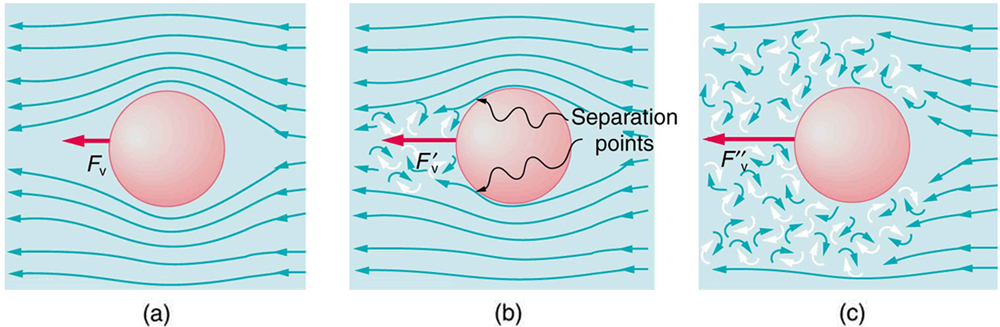
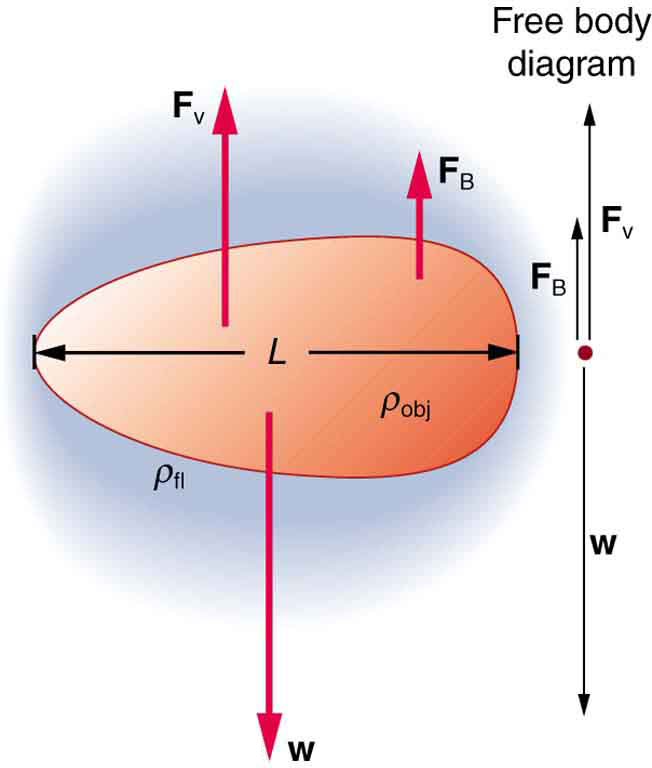
An interesting consequence of the increase in with speed is that an object falling through a fluid will not continue to accelerate indefinitely (as it would if we neglect air resistance, for example). Instead, viscous drag increases, slowing acceleration, until a critical speed, called the terminal speed , is reached and the acceleration of the object becomes zero. Once this happens, the object continues to fall at constant speed (the terminal speed). This is the case for particles of sand falling in the ocean, cells falling in a centrifuge, and sky divers falling through the air. [link] shows some of the factors that affect terminal speed. There is a viscous drag on the object that depends on the viscosity of the fluid and the size of the object. But there is also a buoyant force that depends on the density of the object relative to the fluid. Terminal speed will be greatest for low-viscosity fluids and objects with high densities and small sizes. Thus a skydiver falls more slowly with outspread limbs than when they are in a pike position—head first with hands at their side and legs together.
By measuring the terminal speed of a slowly moving sphere in a viscous fluid, one can find the viscosity of that fluid (at that temperature). It can be difficult to find small ball bearings around the house, but a small marble will do. Gather two or three fluids (syrup, motor oil, honey, olive oil, etc.) and a thick, tall clear glass or vase. Drop the marble into the center of the fluid and time its fall (after letting it drop a little to reach its terminal speed). Compare your values for the terminal speed and see if they are inversely proportional to the viscosities as listed in [link] . Does it make a difference if the marble is dropped near the side of the glass?
Knowledge of terminal speed is useful for estimating sedimentation rates of small particles. We know from watching mud settle out of dirty water that sedimentation is usually a slow process. Centrifuges are used to speed sedimentation by creating accelerated frames in which gravitational acceleration is replaced by centripetal acceleration, which can be much greater, increasing the terminal speed.
What direction will a helium balloon move inside a car that is slowing down—toward the front or back? Explain your answer.
Will identical raindrops fall more rapidly in air or air, neglecting any differences in air density? Explain your answer.
If you took two marbles of different sizes, what would you expect to observe about the relative magnitudes of their terminal velocities?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?