| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The situation would seem different to the astronaut. Because motion is relative, the spaceship would seem to be stationary and the Earth would appear to move. (This is the sensation you have when flying in a jet.) If the astronaut looks out the window of the spaceship, she will see time slow down on the Earth by a factor of . To her, the Earth-bound sister will have aged only 2/30 (1/15) of a year, while she aged 2.00 years. The two sisters cannot both be correct.
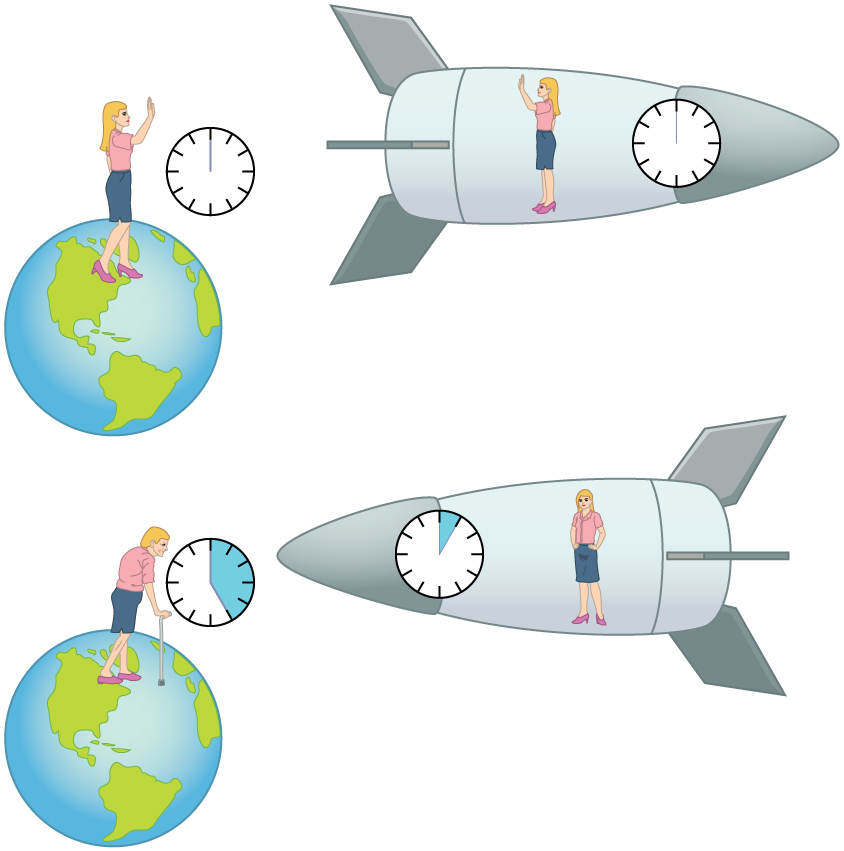
As with all paradoxes, the premise is faulty and leads to contradictory conclusions. In fact, the astronaut’s motion is significantly different from that of the Earth-bound twin. The astronaut accelerates to a high velocity and then decelerates to view the star system. To return to the Earth, she again accelerates and decelerates. The Earth-bound twin does not experience these accelerations. So the situation is not symmetric, and it is not correct to claim that the astronaut will observe the same effects as her Earth-bound twin. If you use special relativity to examine the twin paradox, you must keep in mind that the theory is expressly based on inertial frames, which by definition are not accelerated or rotating. Einstein developed general relativity to deal with accelerated frames and with gravity, a prime source of acceleration. You can also use general relativity to address the twin paradox and, according to general relativity, the astronaut will age less. Some important conceptual aspects of general relativity are discussed in General Relativity and Quantum Gravity of this course.
In 1971, American physicists Joseph Hafele and Richard Keating verified time dilation at low relative velocities by flying extremely accurate atomic clocks around the Earth on commercial aircraft. They measured elapsed time to an accuracy of a few nanoseconds and compared it with the time measured by clocks left behind. Hafele and Keating’s results were within experimental uncertainties of the predictions of relativity. Both special and general relativity had to be taken into account, since gravity and accelerations were involved as well as relative motion.
1. What is if ?
2. A particle travels at and lives when at rest relative to an observer. How long does the particle live as viewed in the laboratory?
where
Does motion affect the rate of a clock as measured by an observer moving with it? Does motion affect how an observer moving relative to a clock measures its rate?
To whom does the elapsed time for a process seem to be longer, an observer moving relative to the process or an observer moving with the process? Which observer measures proper time?
How could you travel far into the future without aging significantly? Could this method also allow you to travel into the past?
(a) What is if ? (b) If ?
Particles called -mesons are produced by accelerator beams. If these particles travel at and live when at rest relative to an observer, how long do they live as viewed in the laboratory?
Suppose a particle called a kaon is created by cosmic radiation striking the atmosphere. It moves by you at , and it lives when at rest relative to an observer. How long does it live as you observe it?
A neutral -meson is a particle that can be created by accelerator beams. If one such particle lives as measured in the laboratory, and when at rest relative to an observer, what is its velocity relative to the laboratory?
A neutron lives 900 s when at rest relative to an observer. How fast is the neutron moving relative to an observer who measures its life span to be 2065 s?
If relativistic effects are to be less than 1%, then must be less than 1.01. At what relative velocity is ?
If relativistic effects are to be less than 3%, then must be less than 1.03. At what relative velocity is ?
(a) At what relative velocity is ? (b) At what relative velocity is ?
(a)
(b) (to five digits to show effect)
(a) At what relative velocity is ? (b) At what relative velocity is ?
Unreasonable Results
(a) Find the value of for the following situation. An Earth-bound observer measures 23.9 h to have passed while signals from a high-velocity space probe indicate that have passed on board. (b) What is unreasonable about this result? (c) Which assumptions are unreasonable or inconsistent?
(a) 0.996
(b) cannot be less than 1.
(c) Assumption that time is longer in moving ship is unreasonable.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?