| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The downward pressure of the uterus also compresses the urinary bladder, leading to frequent urination. The problem is exacerbated by increased urine production. In addition, the maternal urinary system processes both maternal and fetal wastes, further increasing the total volume of urine.
Blood volume increases substantially during pregnancy, so that by childbirth, it exceeds its preconception volume by 30 percent, or approximately 1–2 liters. The greater blood volume helps to manage the demands of fetal nourishment and fetal waste removal. In conjunction with increased blood volume, the pulse and blood pressure also rise moderately during pregnancy. As the fetus grows, the uterus compresses underlying pelvic blood vessels, hampering venous return from the legs and pelvic region. As a result, many pregnant women develop varicose veins or hemorrhoids.
During the second half of pregnancy, the respiratory minute volume (volume of gas inhaled or exhaled by the lungs per minute) increases by 50 percent to compensate for the oxygen demands of the fetus and the increased maternal metabolic rate. The growing uterus exerts upward pressure on the diaphragm, decreasing the volume of each inspiration and potentially causing shortness of breath, or dyspnea. During the last several weeks of pregnancy, the pelvis becomes more elastic, and the fetus descends lower in a process called lightening . This typically ameliorates dyspnea.
The respiratory mucosa swell in response to increased blood flow during pregnancy, leading to nasal congestion and nose bleeds, particularly when the weather is cold and dry. Humidifier use and increased fluid intake are often recommended to counteract congestion.
The dermis stretches extensively to accommodate the growing uterus, breast tissue, and fat deposits on the thighs and hips. Torn connective tissue beneath the dermis can cause striae (stretch marks) on the abdomen, which appear as red or purple marks during pregnancy that fade to a silvery white color in the months after childbirth.
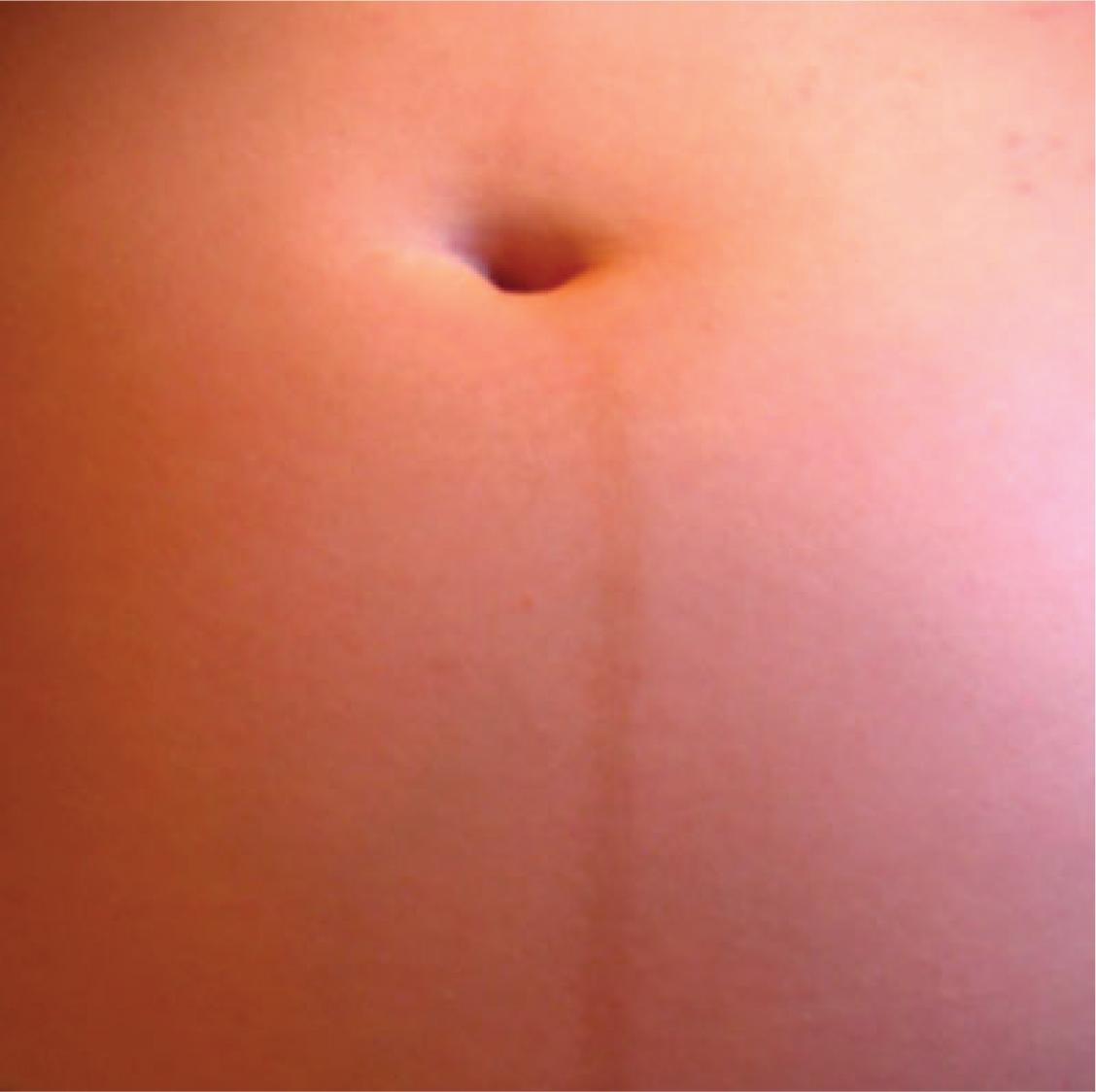
An increase in melanocyte-stimulating hormone, in conjunction with estrogens, darkens the areolae and creates a line of pigment from the umbilicus to the pubis called the linea nigra ( [link] ). Melanin production during pregnancy may also darken or discolor skin on the face to create a chloasma, or “mask of pregnancy.”
Childbirth, or parturition , typically occurs within a week of a woman’s due date, unless the woman is pregnant with more than one fetus, which usually causes her to go into labor early. As a pregnancy progresses into its final weeks, several physiological changes occur in response to hormones that trigger labor.
First, recall that progesterone inhibits uterine contractions throughout the first several months of pregnancy. As the pregnancy enters its seventh month, progesterone levels plateau and then drop. Estrogen levels, however, continue to rise in the maternal circulation ( [link] ). The increasing ratio of estrogen to progesterone makes the myometrium (the uterine smooth muscle) more sensitive to stimuli that promote contractions (because progesterone no longer inhibits them). Moreover, in the eighth month of pregnancy, fetal cortisol rises, which boosts estrogen secretion by the placenta and further overpowers the uterine-calming effects of progesterone. Some women may feel the result of the decreasing levels of progesterone in late pregnancy as weak and irregular peristaltic Braxton Hicks contractions , also called false labor. These contractions can often be relieved with rest or hydration.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?